High quality wood finishes are an essential aspect of woodworking, providing protection, enhancing beauty, and ensuring the longevity of wood surfaces. With various options available, it can be overwhelming to choose the right types of wood finishes for your project.
In this blog post, we’ll explore different types of wood finishes, with a focus on water-based primers, sealers, lacquers, stains, varnishes and polyurethanes.
Sealing / Priming Coats
(Provide a smooth/consistent foundation for what comes next)
1. Pigmented Wood Primer
We’re slotting this (and sealer, below) into “types of wood finishes,” but a wood primer is a preparatory coating applied to wood surfaces before the application of an opaque or deeply pigmented paint or other finishes. It acts as a bonding agent, creating a strong adhesion between the wood and the topcoat for an even and consistent finish. They also help block stains, knots, and tannins, ensuring a smooth and flawless paint application. Wood primers are essential for achieving a durable and long-lasting painted finish on wood projects.
A wood primer like Target Coating’s EMTECH® HSF5000PSFS is a top-quality water-based option designed for open-grained wood, MDF, and engineered veneers. It creates a smooth and non-textured base for pigmented top coats, offering excellent hiding power (see photo below). It can be used as a primer, surfacer, and filler, making it ideal for various woodworking projects. When paired with pigmented water-based wood finishes and stains, it can help create a durable and long-lasting high-quality finish.
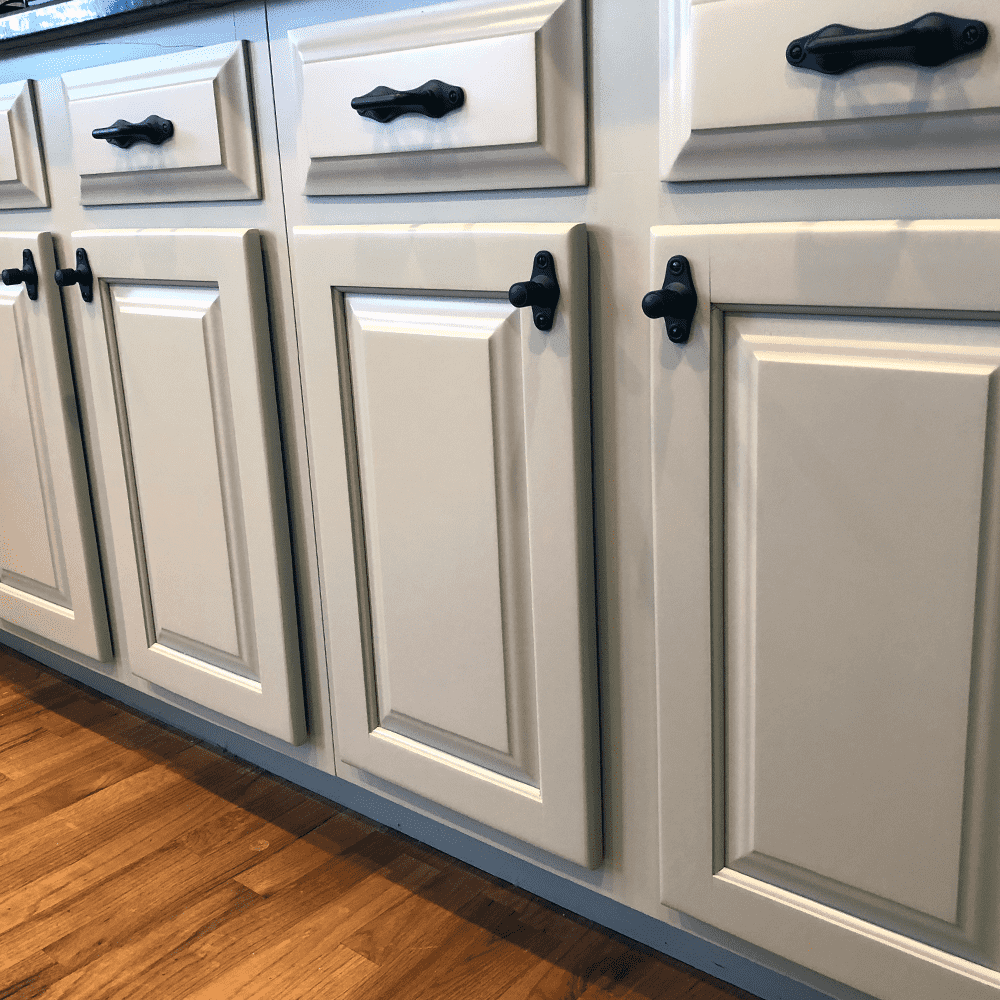

5 Projects Perfect For Pigmented Wood Primers:
1. Furniture Refinishing: When restoring or refinishing wooden furniture, a pigmented wood primer can help create an even base color and improve the adherence of the final paint or finish. This is especially useful when changing the color of the furniture.
2. Exterior Woodwork: If you’re painting exterior wooden structures like fences, decks, or outdoor furniture, a pigmented wood primer can provide added protection against the elements and help prevent the paint from chipping or peeling.
3. Cabinet Painting: If you’re painting kitchen cabinets, bathroom cabinets, or other built-in wooden cabinetry, using a pigmented wood primer can ensure a smoother and more professional finish, particularly when transitioning from a dark to a light color or vice versa.
4. Wood Crafts: For DIY woodcraft projects such as decorative signs, wooden toys, and other small wooden items, applying a pigmented wood primer before painting can enhance the vibrancy and longevity of the paint colors.
5. Indoor Wall Paneling: If you’re dealing with wooden wall paneling indoors, a pigmented wood primer can help create a uniform surface before applying paint or a decorative finish, ensuring that the final result looks polished and well-maintained.
You can read more about primers and sealers here.
2. Clear Wood Sealer
A wood sealer is a protective coating applied to wood surfaces before the application of the final finish. It serves to seal the wood, preventing it from absorbing too much stain or finish, which can result in uneven coloration and reduced durability. Wood sealers are particularly essential for a wide variety of porous woods. They help create a more even surface for subsequent types of wood finishes, ensuring a smoother and more professional appearance. Additionally, wood sealers enhance the wood’s natural grain, adding depth and character to the final finish.
Our EM1000 Universal Sanding Sealer is a very efficient wood sealer. Crafted with water-based technology, it is specially formulated to deeply penetrate the wood’s cell structure, providing enhanced adhesion for a robust and long-lasting finish.
Being user-friendly and ultra-low in VOC’s, EM1000 Universal Sanding Sealer is perfect for the wood finisher who is committed to sustainability in woodworking projects. Moreover, it can be used beneath any interior-grade clear finishes to promote adhesion, elevate natural beauty, and embrace sustainability in your woodworking endeavors.
5 Projects Perfect For Clear Wood Sealers:
1. Hardwood Floors: Applying a clear wood sealer to hardwood floors can help protect them from daily wear, spills, and foot traffic while enhancing the wood’s natural beauty. It adds a layer of durability and makes cleaning easier.
2. Wooden Countertops: If you have wooden countertops in your kitchen or bathroom, using a clear wood sealer can create a protective barrier against water, stains, and heat. It also accentuates the wood’s color and grain.
3. Wooden Staircases: Sealing wooden staircases with a clear wood sealer can prevent scratches, scuffs, and other signs of wear. It maintains the staircase’s appearance and ensures its longevity.
4. Indoor Wood Furniture: Applying a clear wood sealer to indoor wooden furniture, such as dining tables, chairs, and cabinets, can protect them from spills, stains, and daily use. It can also bring out the natural elegance of the wood.
5. Interior Wood Paneling: If you have wooden paneling on your walls, sealing it with a clear wood sealer can safeguard it from moisture, dirt, and general wear. It maintains the wood’s appearance and makes cleaning easier.
Wondering if you can use water-based sealer over an oil-based stain? Here’s the answer…
Base Coats / Coloring Coats
(Often control 95% of your color and “look”)
3. Wood Stains
OK, the next types of wood finishes are wood stains. Wood stains are either dye or pigment-based colorant binders used to enhance the color and appearance of wood surfaces. They penetrate the wood’s pores, highlighting its natural grain and providing depth and character to the finish. Wood stains come in various colors, allowing woodworkers to achieve a wide range of looks, from light and subtle to dark and dramatic. They are popular for adding warmth and richness to furniture, flooring, and other wood projects. Proper application and choice of stain can significantly impact the final aesthetic, making wood stains an essential tool in the woodworking arsenal.
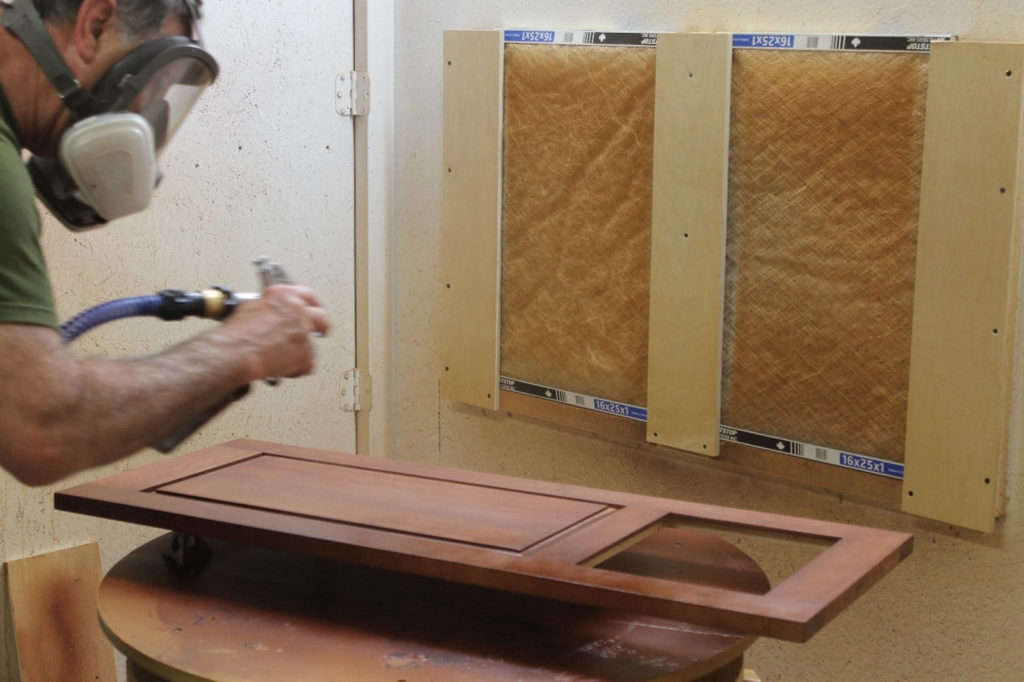

Enhancing or altering the color of wood is a powerful and creative tool in the world of woodworking. However, choosing the right type of wood stain can be a significant decision, with several considerations to keep in mind. Wood stains are generally categorized into dye-based, pigment-based, or dye/pigment blend stains, each with unique characteristics and effects on the wood they are applied to.
Dye stains are excellent for creating base colors, offering high color strength and suitability for shading and toning. They are made from chemical reactions with organic compounds and metals, resulting in very small particle sizes that deeply penetrate the wood’s cell structure. Dyes are highly transparent, even at high concentrations, making them ideal for adjusting underlying color tones. However, they tend to have moderate fade resistance when exposed to prolonged UV light.
On the other hand, pigment-based stains consist of ground oxides with much larger structures. Even at low percentages, pigments create translucency, while higher concentrations lead to opacity, allowing them to hide the wood’s natural features. This makes them suitable for adjusting or concealing wood grain effects. Pigment-based wood stains are generally more fade-resistant when exposed to UV light.
Wood stains can also be blends of both dye and pigment, combining the strengths of each type. They are available in water-based or oil-based formats, with some products specifically labeled as dye-based or pigmented stains. Water-based dye stains, like Target Coatings’ NR4000 and Mohawk Dye Stains, are commonly used for furniture, cabinet, and trim finishing. Meanwhile, pigmented stains, such as Cabot, Flood, and Sikens, are typically found for deck and siding applications.
In recent practice, many finishers prefer using water-based dye stains over oil-based stains to act as color shades or toners. This allows for greater control over the final color and appearance of the wood. As you shop for wood stains, it’s crucial to consider the type and format that best suits your project’s needs, ensuring you achieve the desired outcome and enhance the natural beauty of the wood.
5 Projects Perfect For Wood Stains:
1. Cabinet Refinishing: Applying wood stain to kitchen cabinets, bathroom cabinets, or other built-in cabinetry can give them a fresh look while retaining the wood’s natural beauty. Staining allows you to change or deepen the color of the wood.
2. Wooden Furniture Restoration: When restoring or refinishing wooden furniture pieces, using wood stain can help you achieve the desired color and tone. Staining can revitalize older pieces or give new furniture a unique look.
3. Interior Trim and Molding: Staining interior trim, baseboards, crown molding, and other architectural details can add warmth and depth to your home’s interior. It helps create a cohesive and elegant look.
4. Wooden Floors: Staining hardwood floors can transform the appearance of a room. Whether you want a classic, rich color or a more contemporary look, wood stain can help you achieve the desired aesthetic.
5. Doors and Door Frames: Applying wood stain to interior doors and door frames can complement the overall design of your home. Staining these elements can create a seamless flow and enhance the interior’s visual appeal.
Read more about getting beautiful results with water based stains, here.
4. Clear Lacquer
A common terminology for many different types of clear coats for use on wood and metal, lacquer is a type of finish commonly used on these surfaces to enhance appearance and provide protection.
It is a clear or colored coating that forms a hard, durable film when applied. Lacquers can be solvent-based or water-based, and they offer varying levels of sheen, from matte to high gloss. They are favored for their fast-drying times and ease of application, making them popular choices for furniture, cabinets, and decorative pieces. Lacquers are known for their ability to bring out the natural beauty of the material they are applied to.
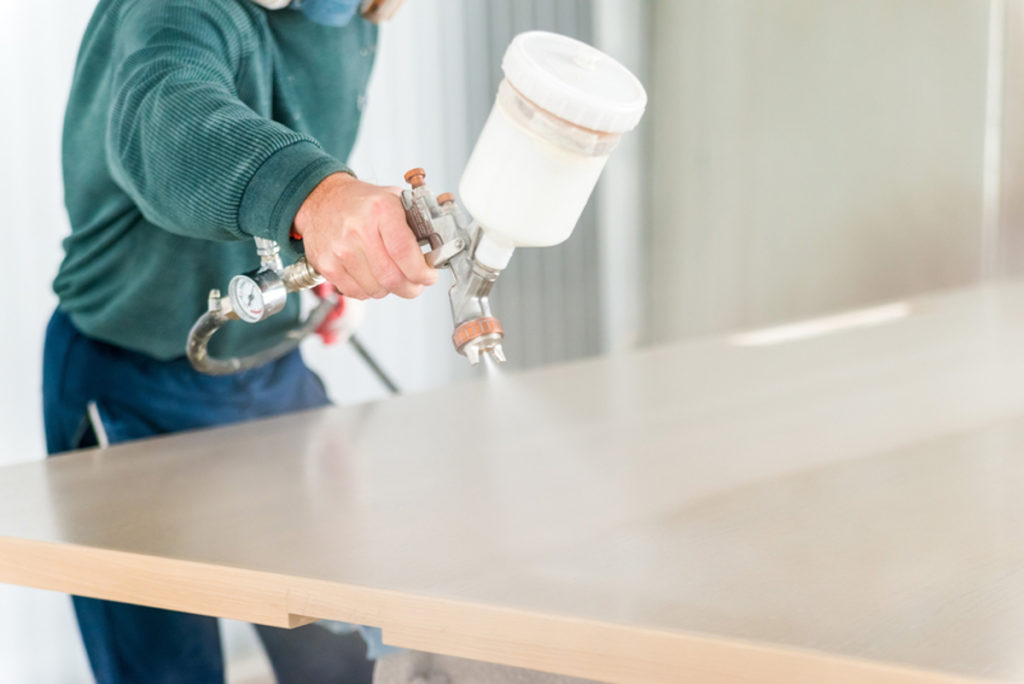

Water-based lacquers are becoming increasingly popular types of wood finishes due to their low VOC content and environmental friendliness. Target Coatings’ EM7000HBL High-Build Water-Based Lacquer is a prime example. This lacquer offers excellent durability, fast drying time, and a high-build formula that reduces the need for multiple coats. It is suitable for furniture, cabinetry, and other interior woodworking projects.
4 Projects Perfect For Clear Lacquer:
1. Wooden Furniture: Applying clear lacquer to wooden furniture can protect it from wear and tear while enhancing its natural beauty. It provides a durable finish that is resistant to water, stains, and scratches, making it ideal for pieces that receive frequent use.
2. Cabinetry: Clear lacquer can be used on kitchen cabinets, bathroom cabinets, and other built-in cabinetry. It adds a protective layer that is easy to clean and maintains the wood’s appearance over time.
3. Wooden Countertops: If you have wooden countertops in your kitchen or bathroom, clear lacquer can provide a water-resistant and durable finish that protects the wood from spills, stains, and heat.
4. Decorative Woodwork: For decorative wooden items like sculptures, carvings, and intricate wood designs, clear lacquer can highlight the details while providing a protective layer against environmental factors.
Want to FULLY understand what a “lacquer” is…and isn’t? Read this…
5. Pigmented Lacquer Paint
Lacquer paint is another type of wood finish that combines the qualities of traditional lacquer with the convenience of paint. It is typically a water-based or solvent-based coating that forms a durable film when applied to surfaces like wood, metal, or plastic. Pigmented lacquers offers a smooth, glossy finish and dries relatively quickly, making it popular for kitchen cabinet, architectural trim, and furniture refinishing projects. These types of wood finishes provide a protective layer that enhances the appearance of the object, offering both aesthetics and durability in one versatile product.
Water-based lacquer paint, such as Target Coatings’ EM6500 Pigmented Lacquer, is favored by woodworkers for its convenience and exceptional performance. This wood finish adheres to stringent environmental regulations due to its lower VOC levels, ensuring a durable and aesthetically pleasing result without compromising indoor air quality. Application methods vary, with spraying being ideal for large surfaces, while brushing or rolling suits smaller projects or intricate details. Proper ventilation and safety gear are essential during application, with multiple thin coats and sanding between layers recommended for achieving a smooth surface.
5 Projects Perfect For Pigmented Lacquer Paint:
1. Furniture Refinishing: Pigmented lacquer paint can be used to refinish wooden furniture, giving it a fresh coat of color while also benefiting from the lacquer’s protective and durable finish.
2.Cabinet Makeover: If you’re looking to update the look of your cabinets, pigmented lacquer paint provides a smooth and glossy finish that can transform their appearance and provide long-lasting protection.
3. Trim and Molding: Painting interior trim, baseboards, crown molding, and other architectural details with pigmented lacquer paint can create a polished and cohesive look throughout your home.
4. Doors and Door Frames: Pigmented lacquer paint is a great choice for painting interior doors and their frames. It provides a smooth and even finish that can withstand daily use.
5. Wooden Decor and Accents: For wooden decorative items like picture frames, shelves, and wooden accents, pigmented lacquer paint offers vibrant color and a protective layer that maintains the wood’s integrity.
Read more here about the compatibility of pigmented lacquers.
Top Coats / Finish Coats
(Mainly determine overall protection, sheen, and coloration over time)
6. Varnishes
Of all the types of wood finishes, the term “varnish” may have just as many uses and variables as the word lacquer does. Varnish, one of Humanities oldest surface coatings, has been used to protect everything from sailing ships to exotic furniture. Varnish in its basic form is made from a variety of organic oils that are blended with solvents and metallic driers to create a film forming finish that can offer a range of protective qualities. These oils can be linseed, castor, tung or safflower in origin. When properly formulated each offers a different color tone as it ages in a clear format. Also, these oils can be used as the resin vehicle for finely ground pigments to create alkyd paints. The solvents used in the blending of these oils range from turpentine (turps) mineral spirits and other aromatic hydrocarbon solvents.
While varnishes are still looked upon as being oil based, there has been a wide array of oil/water “hybrid” varnishes that have slowly come onto the market since the mid-1990’s. The hybrid varnishes offer the same depth of color and richness common to the old-world long-oil varnish but without the extremely long dry time, fumes and combustibility. Even more intriguing is that hybrid varnishes will dry and can be recoated in 1/8th the time required for true oil-based varnishes to be approached for extra coats. Modern hybrid varnishes such as EM2000wvx Waterborne Alkyd Varnish is as excellent example of a well formulated hybrid alternative to dangerous solvent-based finishes.
7. Urethane and Polyurethane
There are water-based and oil-based urethanes and polyurethanes, and all of these types of wood finishes are used mainly for their superior ability to withstand abrasion, impacts, moisture, and chemical exposure. If those protective qualities sound a lot like “varnish” above, you’d be right — urethanes and polyurethanes are basically synthetic, man-made alternatives to varnish.
Urethanes and polyurethanes are effective on a molecular level because their long chains of polymers interlock and crosslink, creating a tight network that adheres firmly to the surfaces they are applied to and produces a dense and sturdy film barrier.
What’s the difference between the two? Urethanes tend to produce a more “flexible” finish, often making them better suited to exterior applications exposed to the constantly changing elements. Polyurethanes tend to produce a “harder” coating that might chip or crack outdoors, but they are well suited to more “stable” interior environments.
A very important subset of polyurethane is 2K Polyurethane.
These two-part polyurethanes, also known as “2-pack” or “2K-PU,” consist of two components mixed together before application. The appeal of these products lies in their superior durability and higher solids, which can lead to enhanced physical performance and potentially fewer coats required.
Notably, 2K waterborne polyurethanes and 2K waterborne conversion varnishes have gained popularity for their performance in high-demand environments. However, there is a significant concern regarding the use of two particular types of catalyst – a highly toxic and reactive isocyanate based on Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), and hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI). These catalysts are is being used by untrained finishers in poorly ventilated spaces, raising serious health and safety issues.
The lack of information surrounding the downsides of these products, particularly their health and safety profiles, is alarming. While social media is abuzz with 2K polyurethane discussions, few are addressing the potential risks and proper handling guidelines.
In light of this, a conscientious research project is underway to gather facts and provide a better-informed opinion on these products. Rather than seeking attention or clicks, the focus is on understanding the real implications and ensuring proper education.
In conclusion, while certain types of 2K polyurethanes offer unique benefits in terms of performance and application, it is vital to highlight the potential hazards associated with specific catalysts and ensure that knowledge is disseminated appropriately to safeguard the health of both finishers and the environment.
For a deeper dive, check out this post on 2K polyurethanes.
Happy Finishing!
Wood finishing not only enriches wood’s natural beauty by accentuating its grain and color but also safeguards it from wear, moisture, and environmental factors.
Whether it’s revitalizing furniture, preserving outdoor decks, or adding elegance to interior spaces, wood finishing combines aesthetics and functionality. The choice of finish depends on the project’s requirements, from the rich warmth of stains to the glossy protection of lacquers, all contributing to the lasting allure of wood.
I hope this list will help you find the perfect finish type for YOUR project.
If you have questions about this guide to types of wood finishes…or comments / suggestions on how to make it better…
Please share your thoughts or read what others are saying in the COMMENTS SECTION below.
— Jeff Weiss


Good article Jeff. Learned some things from it.
Great write . Thx
Thanks for your comment. We are glad to hear you enjoyed this article.
-SK